Competition Law Legal Update (July 2023)

Top Read: Japan Editor, July 2023
In order to obtain a physical copy of this article, you simply need to have an account or log in on Mondaq.com.

JFTC Reveals FY2022 Antitrust Violation Cases
Yoshiharu Usuki and Hiroki Kitada
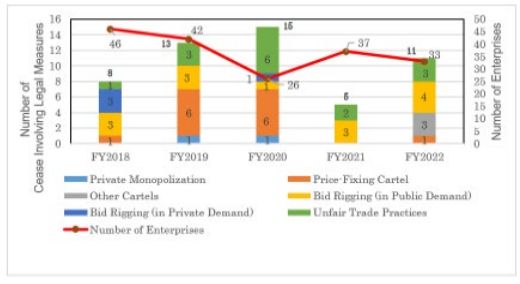
In June 1, 2023, the Japan Fair Trade Commission (JFTC) released a document titled "Processing Status of Cases in Violation of the AMA in FY2022." With the decline of the COVID-19 pandemic, there has been a significant increase in legal actions, resulting in a record-breaking surcharge amount of ¥101.9 billion ($890.9 million). The report highlights the investigation of bid-rigging cases in the electricity and event industries, as well as the first public announcement of a case utilizing the surcharge reduction system. In the next section, we will provide a brief overview of the JFTC's handling of these antitrust cases. Following the decline of the COVID-19 pandemic, there has been a notable rise in cases involving legal measures, leading to a record high surcharge amount of JPY 101.99 billion (approximately USD 731.76 million) in FY2022. The report focuses on the investigation of bid-rigging cases in the electricity and event sectors, as well as the first public announcement of a case utilizing the surcharge reduction system. We will now provide a brief comment on the progress of the cases that violate the AMA, as published by the JFTC.
1.1 Patterns in Cease and Desist Orders
During the fiscal year 2022, there were 11 legal actions implemented, which consisted of 8 orders to cease and refrain from certain activities. These orders were comprised of 1 instance of price-fixing cartel, 3 instances of other types of cartels, 4 cases of bid rigging in public demand, and no cases of bid rigging in private demand. Additionally, there were 3 approval granted for commitment plans in relation to unfair trade practices. It is worth noting that this represents a notable rise compared to the total of 5 cases in fiscal year 2021.

(Source: The JFTC "Status of Cases in Violation of the Antimonopoly Act in the Fiscal Year 2022" (June 1, 2023) page 2)
(Alternative 1) Additional cartels refer to cartels related to volume, distribution networks, limitations on consumer mobility, facility constraints, and so on. (Alternative 2) Different cartels are cartels that encompass factors like quantity, distribution methods, restrictions on customer mobility, facility limitations, and more. (Alternative 3) Diverse cartels are cartels that encompass various aspects such as quantity, sales channels, limitations on customer movement, facility constraints, and so forth.
(Alternative words) Approval of the commitment plan refers to an administrative decision made under the AMA, where the JFTC gives its approval to a commitment plan that has been submitted by a company that has received the Notice of Commitment Procedures. If the JFTC determines that the approved commitment plan is not being followed, it may decide to revoke the approval and resume the investigation procedure that was conducted prior to the issuance of the Notice of Commitment Procedures.
(Alternative) Legal actions encompass cease and desist orders, orders to pay surcharges, and approvals of commitment plans. If both a cease and desist order and a surcharge payment order are issued in a particular case, it is considered as a single legal action.
(Revised) The instances that qualify as both private monopolization and unfair trade practice are classified as "Private monopolization".
The surge in legal cases during FY2022 can be attributed to the COVID-19 pandemic, which imposed constraints on economic and investigative endeavors, resulting in limited operations.
In the fiscal year 2022, there were significant legal actions taken against large-scale cartel and bid rigging cases. The Japan Fair Trade Commission (JFTC) issued cease and desist orders and surcharge payment orders against the former general electricity utilities and others on March 30, 2023. Additionally, on February 28, 2023, the JFTC made a criminal accusation regarding bid-rigging related to the outsourcing contracts for planning test events of the Olympic and Paralympic Games Tokyo 2020, which were ordered by the Tokyo Organizing Committee of the Olympic and Paralympic Games. In regards to the former case, the JFTC required the business operators involved to pay a surcharge totaling around JPY 101 billion. This resulted in the highest amount of surcharges ever collected in a single fiscal year, which occurred in FY2022.
Another important point to mention is the reaction to actions that unfairly harm small and medium-sized businesses ("Notification regarding the discontinuation of Product Guide Production Fee in PB manufacturing contract by SEVEN-ELEVEN JAPAN" dated December 22, 2022). Additionally, even though it was not publicly disclosed, the JFTC has given a caution to a business operator who informed their contracted illustrator that if they choose not to become a taxable business operator after the invoice system is implemented, and instead opt for a tax-exempt business operator, 10% of the transaction value will be deducted, which matches the consumption tax rate.
To read the complete blog post, click on this link.
The information presented in this blog aims to offer a basic overview of the topic. It is important to consult with an expert regarding your individual situation.
Well-liked posts about: Anti-monopoly/Legal measures related to fair competition in Japan.
Examining The Competition (Amendment) Act, 2023
On April 3rd, 2023, the Rajya Sabha, the Upper House of the Indian Parliament, approved the Competition (Amendment) Bill, 2023 (Bill No. 185-C of 2022), aiming to suggest substantial modifications...









































